11 Types of scientific changes with examples
11 Types of scientific changes with examples
Hey everyone, I hope you'll read my previous blog on Equilibrium and found it helpful. So today I have come up with another such topic: physical and chemical changes. In this blog I will discuss only a few changes mentioned in the list below. The others will be dealt in another part otherwise the post will get too long So lets dive in
- Types of changes and examples:-
- Physical change
- Chemical change
- Natural change
- Reversible change
- Irreversible change
- Useful change
- Harmful change
- Quick change
- Slow change
- Periodic change
- Non-Periodic change
Physical changes :
Physical Changes are a particular change that occurs in a substance. However in Physical changes there is no change hat occurs in the chemical composition of that very substance nor does the substance lose or gain any other chemical property. The only visible and noticeable change that occurs is in its physical properties. Application of the properties of Physical changes is sometimes used for separating components from their mixtures
Everyday life Examples :
- Evaporation [ vapor being generated from a liquid ]
- Drying of clothes
- Formation of salt from seawater
- Process of Dissolution
- Boiling
- Melting, etc
Other examples :
- Crushing of cans
- Shredding paper
- Chopping wood

Chemical Changes :
Chemical changes can be said to be something quite opposite to Physical Changes. In this type of change the body going through it experiences a total change in its chemical compositions and it gets new chemical properties. In such cases where the change happening is a chemical change, a completely new substance is formed with new properties. Many a time such Chemical Changes are irreversible. We will discuss what irreversible changes are later in this blog.
Everyday life Examples :
- Ripening of fruits
- Turning of sugar into caramel
- Burning wood [ at the end only ash is left and its properties are different than that of wood and hence it is a chemical change ]
Instances only viewed in laboratories :
- Forming of compounds from their constituent elements
- Forming of water
- The change of color observed when testing acids and bases with litmus paper

Natural changes :
Natural changes are changes that occur naturally in nature. These changes take place naturally and don't have the participation of any human activity. Natural changes have a huge impact on our daily lives. Many times these changes are quite useful and beneficial for humans while on other times they create huge devastation
Everyday life examples :
- Ripening of fruits
- Spoiling of milk
- Growth of any living thing
- Environmental changes
- Seasonal changes
- Falling of leaves and many more

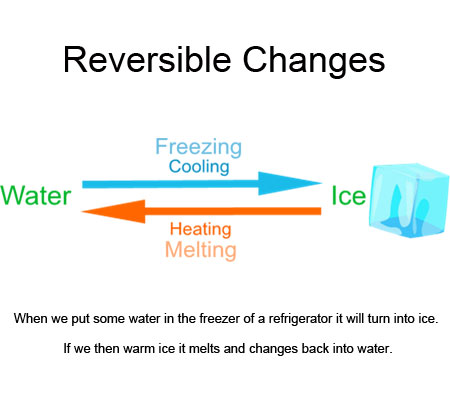
Reversible Changes :
Reversible changes are a very basic and important type of change that occurs quite frequently and can be observed in our surroundings. As the name suggests, such types of changes are reversible in nature. Reversible change means a type of change that can be reversed to get access to the original substance again. Reversible changes occur in both forward and reverse action and that too quite a lot of times. That means this process can be done many times. There are quite a lot of reverse reactions in chemistry as well but in many of those the process finally reaches Dynamic Equilibrium and completely stops. I have written a complete article on Dynamic Equilibrium so I won't discuss them now. If interested click here to read that article. However all the changes are not reversible. But science is trying to achieve this feat.
Everyday life examples :
- Melting
- Boiling
- Freezing
- Changing the shape of a particular object
- Melting and solidifying wax again and again
Examples of reverse reactions in Chemistry :
- The process of Hydrogen and Iodine forming a compound called Hydrogen iodide [ Hi ]
Irreversible changes :
As the name suggests, these changes are exactly the opposite of reversible changes. In such a change the reaction only happens in one direction, that is forward. Due to this there is no reaction taking place in the backward direction and these changes are not reversible. Hence such changes are called Irreversible changes. We can observe many such Irreversible changes taking place in our surroundings. We can also call the changes caused by irreversible reactions to be permanent in nature. The majority of chemical changes are irreversible. The only few exceptions are cases in which the chemical reaction reaches Equilibrium.
Everyday life examples :
- Cooking
- Baking
- Frying
- Rusting / Corrosion
- Burning
Examples in chemistry :
- Forming of compounds from individual elements
- H + O2 = H20
- 2Na + H2O = 2NaOH +H2
- CH4 + 2O2 = Co2 + 2H20 [ Combustion ]

Useful Changes :
Changes are actually happening all around us even though if we don't
observe them. Some of these changes are quite useful for us while some
our not. These changes which are useful are called as Useful changes.
These useful changes refer to being beneficial for us.
Examples :
- Baking Bread
- Cooking food
- Switching on Fan
- Recycling materials

Harmful changes :
As mentioned in its name itself, Harmful changes are naturally / man
made changes which prove to be harmful for us. These changes are exactly
opposite to Usful changes. Harmful changes also keep occuring in the
world and are quite often noticeable.
Examples :
Natural :
- Storms
- wildfires
- Tsunmies
- Earthquakes
Man made :
- Pollution
- Deforestation
- Global warming
Quick/Fast Changes :
Not all the changes in this world ocur at the same speeeds. there is a
variation in the time taken for completion of anything or simply a
variation in speed. Considering this there must be different speed
intervals for different Physical and Chemical changes. Well so these
changes can be considered as fast changes. As the name suggests, fast
changes are changes with really low time intervals meaning more speed.
These changes occuring at really high speeds , the change occured can be
observed instantly but the change taking process is not observable.
Examples
Bursting of a balloon
Landslides
Earthquakes
Volcano Eruption
Slow Change :
Slow changes are the ones opposite to Fast changes. These changes are
the ones which take more time to complete. These changes have high time
intervals which gives it less speed. If you just get into deep enough in
this topic then you will understand that these slow changes are more of
a gradual change which occur slowly over the period of time. Unlike
fast changes , these changes occur it more slowly and gradually and
hence are not much observable. While the process of the change taking
place can be easily viewed.
Examples:
- Ripening of fruits
- Changing water into ice and vice versa
- Germination
- Corrosion
- Burning of a candle

Periodic Change :
Periodic changes are changes which occur continuously at fixed time
intervals. That is Periodic Changes occur at constant tie intervals.
Periodic changes occur all around us and are quite observable because
they keep happening at constant time intervals and so that creates a
pattern of strings. Studying those patterns , one can also predict when
that Periodic change will occur again.
Examples
An high tide followed by Low tide and vice versa
Sunrise followed after nighttime and vice versa
Beating of Heart
Non Periodic Changes :
On the contrary of Periodic Changes, some changes are such that their
occurrence cannot be determined. These changes don't take place at fixed
time intervals, instead these changes can occur at any time interval.
As they don't have a fixed occurring time nor do they have any occuring
rate ; these changes don't really make any sort of patterns and it is
hard to predict them. Well if studied in very detail, a few patterns may
emerge and this may lead to that change being Periodic instead of
Non-Periodic. In earlier times the science behind eclipses was not known
so it was Non-Periodic change, but now the science behind its
occurrence is known to us and hence it now considered to be an Periodic
Change. by the way if interested to learn the science of occurrence of
eclipse then click here. You will be diverted to another blog post
written by me which covers everything about eclipses.
Examples :
- A bird sitting on a tree flying away
- Meteor flashing across the sky
- Volcano Eruption
- Burning of matchsticks
So friends we will discuss complicated theorums like Time Diliation from the next blog which will be released on 7th May 2020 / 7 - 5- 2020 . So be sure to come back for reading it.You'll can also read my blogs on startofuniverse.blogspot.com
Till then goodbye and stay home stay safe!
Comments
Post a Comment