Discussing Equilibriums !!!
Discussing Equilibrium
Equilibrium is a very interesting concept in chemistry which is actually related to the laws of opposing forces. And I hence prefer you'll to take a look at my previous blog on forces and Newtonian physics so that you'll will get a better understanding of this concept. So know lets dive - in !!!
Newton's third law of motion :
I hope that you'll went through my previous blog on forces and Newtonian physics but if not then do read this paragraph. Newton was a brilliant scientist of the 1700's period. He in his times formulated the famous laws of motion. Laws of motion is a set of 3 laws of which understanding the 3rd one is important for understanding Equilibrium.
According to the 3rd law of motion formulated by Newton , Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. According to this law it is proved that any object which observes pressure / force will revert equal amount of pressure / force back.
What is Equilibrium :
Equilibrium is state in which the reactant [ force applied on a body ] and resultant [ force reverted back by the body ] forces are equal. Though in Equilibrium the both the opposing forces balance each other out at the same rate they are present on a very minute scale and hence the changes in the matter or even the properties of the matter are not quite observable even with electron microscopes [ most powerful microscopes which can magnify up to x500000 ]. This makes the in depth study of Equilibrium quite difficult as observations cannot be made. Even so , we definitely know that when opposing forces are balanced in chemical terms then there is a Equilibrium which forms.
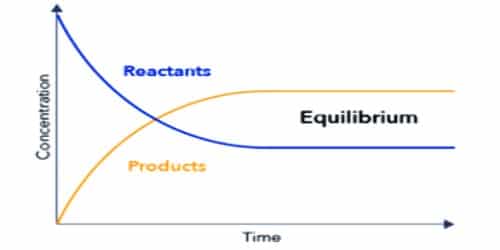
Chemical or Dynamic Equilibrium :
But Equilibrium is not so simple as we think it to be. Study has shown that in equilibrium especially which are formed in chemical experiments , the process of forming of new chemical with different properties happens simultaneously with them breaking and reverse reactions / reversible changes taking place resulting them to form the original / initial chemicals once again.
A brilliant example of such an Chemical Equilibrium is , when you form compound of Hydrogen iodide [HI] from the elements Hydrogen [H+] and Iodine [I-] in a closed area so that exchange of gases does not occur and what happens is only exchange of energy. When you are doing this experiment you'll wont be able to observe the Chemical Equilibrium as we mentioned above that Equilibrium takes place on a very small scale.
But scientists have drawn some conclusions from such experiments. Scientists say that when the reaction begins there is a high proportion of Hydrogen [ H ] and Iodine [ I ] as independent elements. But with time they move through chemical bonding and slowly start to form the compound Hydrogen iodide [ HI ]. With time the proportion of [HI] increases then that of the independent elements and at that time the reverse reaction starts taking place. This very point at which this reaction starts is what we call as Equilibrium.
After the reverse reaction starts , the compound is slowly decomposed and again the proportions of Hydrogen [H] and Iodine [I] as independent elements increases. Then again they form compounds of Hydrogen iodide [HI] and the process continues. But this process continues for a finite / limited amount of time. Later all these 3 components remain at specific proportions and don't change thereafter. And this is the end of this stage .

So friends in this blog we discussed dynamic Equilibrium. In the upcoming blogs we will discuss about static Equilibrium. So do come back for reading them. Also subscribe to our blogs for getting notified about our newest posts !!!
Comments
Post a Comment